Modeling Type 1 Diabetes Using Human Stem Cells in the Brehm and Greiner Labs
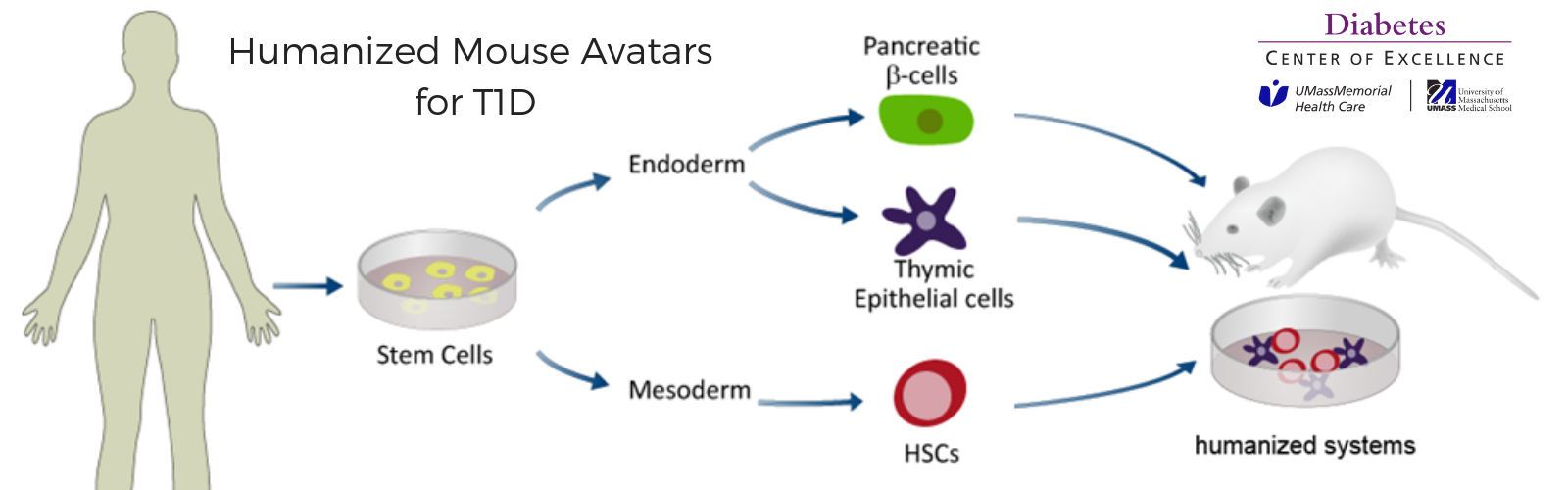
The research team at the UMass Diabetes Center of Excellence (DCOE) continues to gain new knowledge of type 1 diabetes (T1D) by studying human tissues and human cells, to recreate the human immune system. Understanding what causes diabetes will allow researchers to develop effective therapies, and ultimately find the cure.
One of the challenges to uncovering the root causes of T1D, is the inability to access the human tissues required to identify exactly when a person’s immune cells begin attacking their own insulin producing beta cells.
Protocols developed by UMass DCOE co-directors, David Harlan, MD, and Dale Greiner, PhD, research in the lab of Michael Brehm, PhD, and a collaboration with the Melton Lab at The Harvard Stem Cell Institute, allowed the scientists to model type 1 diabetes autoimmunity using patient’s blood and stem cell derived beta cells.

Donated blood was obtained from UMass Diabetes Center of Excellence patients who agreed to participate in a clinical study. Some of the donors had T1D, while others did not have diabetes. Dr. Harlan used his approved protocol to obtain cells from these individuals. Their blood cells were turned into stem cells from which stem cell-derived pancreatic islets are created. One technique enhanced the clusters into glucagon producing alpha-like cells, and another technique turned them into insulin producing beta-like cells. Dr. Greiner has an approved protocol to utilize the immune cells donated by the same donors.
 Their data was published in Cell Reports, titled “Modeling Type 1 Diabetes In Vitro Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.”
Their data was published in Cell Reports, titled “Modeling Type 1 Diabetes In Vitro Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.”
“For decades, clinician scientists like myself have been working to develop methods to safely interfere with the autoimmune response that targets the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreases of people with type 1 diabetes,” said Dr. Harlan. “We’ve dreamed about finding ways to test therapies using assays other than expensive and potentially risky clinical trials, which also take a very long time to conduct”
This new assay provides hope that scientists will be able to successfully conduct in-depth studies into the central autoimmune phenomenon underlying T1D.
“We continue to make great strides looking at the interaction between human immune cells and human beta cells in vivo, using our unique humanized mouse models here at the UMass DCOE,” said Michael Brehm, PhD, co-director of the Humanized Mouse Core Facility at UMass Chan Medical School. “For the first time, we’re studying how the immune system of a person living with diabetes interacts with their own pancreatic beta cells - the cells that make insulin to control blood sugar levels.”
Dr. Brehm is an immunologist at the UMass DCOE, who also lives with T1D. He was diagnosed while earning his PhD. The focus of his diabetes research is to understand the biology of how human insulin-secreting beta cells die during the development of T1D, and how a human immune system mediates the destruction of human beta cells.
“While this new assay will require further testing and development, the work appears to be an encouraging and important step towards the desired cure for T1D,” added Dr. Harlan.
Related Articles
Modeling and Studying the Autoimmune Processes of Human Type 1 Diabetes Using Human Cells and Tissue
Modeling Type 1 Diabetes Using Human Stem Cells in the Brehm and Greiner Labs
