Artificial Intelligence in MRI
Artificial Intelligence algorithm promises faster MRIs with better image quality
There is great interest in leveraging AI to produce a high quality MRI, faster. Historically, methods for making MRI faster also degrade image quality. This fall, UMass will be one of the first sites in the United States to implement a deep learning based MR image reconstruction algorithm from GE Healthcare as part of our ongoing partnership with Shields. This technology, developed to allow faster MR image acquisition at 3T without compromising image quality, received FDA approval only five months ago. GE estimates nearly a 30-40% reduction in scan time for some of our most commonly performed MRIs.
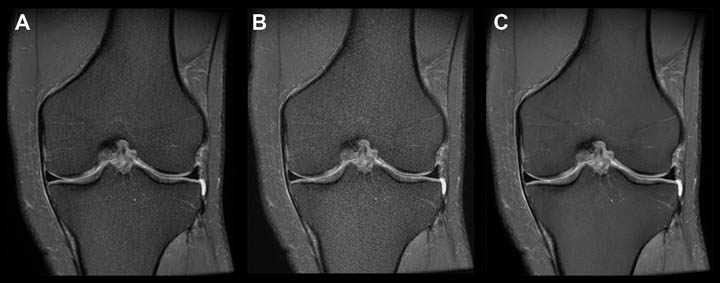
- Knee MRI current image quality, this sequence takes a little over 2 minutes to perform.
- Image quality is visibly degraded when the protocol is adjusted to decrease scan time to 1 minute using conventional methods.
- Image quality is sharper and less noisy when scan time is decreased to 1 minute and the images are reconstructed using the machine learning algorithm.
Data collected at Shields Framingham in collaboration with GE Healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence at work in the Emergency Department
UMass is piloting several FDA approved AI algorithms developed by aidoc, a vendor specializing in diagnostic algorithms that highlight acute abnormalities on CT. This AI based software runs in the background as the radiologist works, flags a case in the reading queue as high priority if an abnormality is detected and produces a color coded overlay to indicate the abnormality.
“..aidoc can be nice, to increase confidence in your work especially when it is busy, but double checking the algorithm’s output can slow you down since it sometimes incorrectly highlights normal findings.” Ganesh Joshi, MD
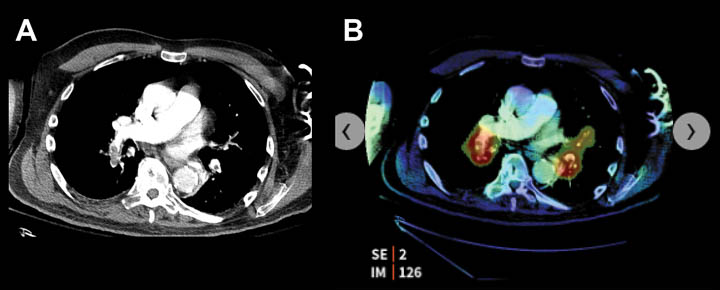
- CT angiogram of the chest with bilateral pulmonary emboli.
- AI based software highlights the emboli, color coded in red.
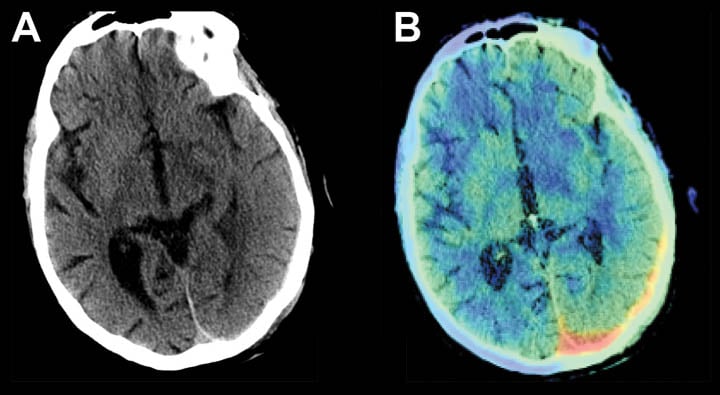
- Subtle, isointense, left subdural hemorrhage on head CT.
- AI based software highlights the area of hemorrhage, color coded in red.
Data collected at UMass Memorial Healthcare in collaboration with aidoc.