Cellular responses to mechanical strain are critical for regeneration, and tissue homeostasis, and are frequently mis-regulated in cancer. Understanding how these processes work is important for devising approaches for organ regeneration and cancer treatment.
 The ability of the LIMD1 and TRIP6 LIM domains to bind strained f-actin is critical for their tension dependent localization to adherens junctions and association with the Hippo pathway kinase LATS1
The ability of the LIMD1 and TRIP6 LIM domains to bind strained f-actin is critical for their tension dependent localization to adherens junctions and association with the Hippo pathway kinase LATS1
Ray, S., DeSilva, C., Dasgupta, I., Mana-Capelli, S., Cruz-Calderon, N, McCollum, D.
Cryoskeleton (Hoboken) Sep 2024. Epub March 2024. PMCID: PMC11366040.
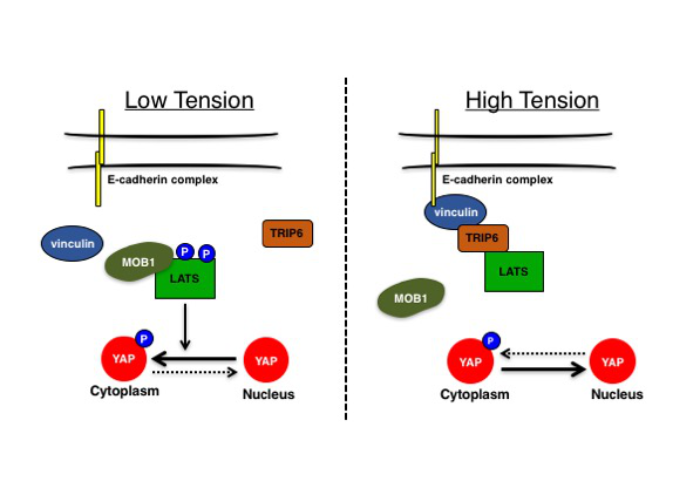 TRIP6 inhibits Hippo signaling in response to tension at adherens junctions
TRIP6 inhibits Hippo signaling in response to tension at adherens junctions
Dutta, S., ManaCapelli, S., Paramasivam, M, Dasgupta, I., Cirka, H., Billiar, K., McCollum, D.
EMBO Rep 2018. PMCID: PMC5797958
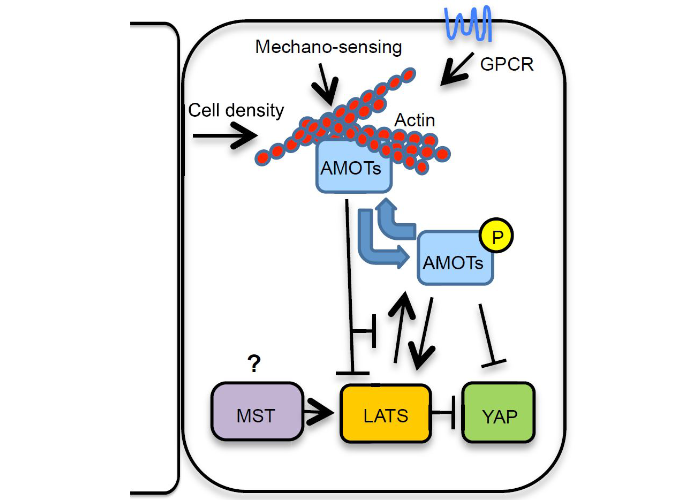 Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling
Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling
Mana-Capelli, S,Paramasiva, M, Dutta, S., McCollum, D.