Mechanisms of Translation Regulation
Rescue of Stalled Ribosomes
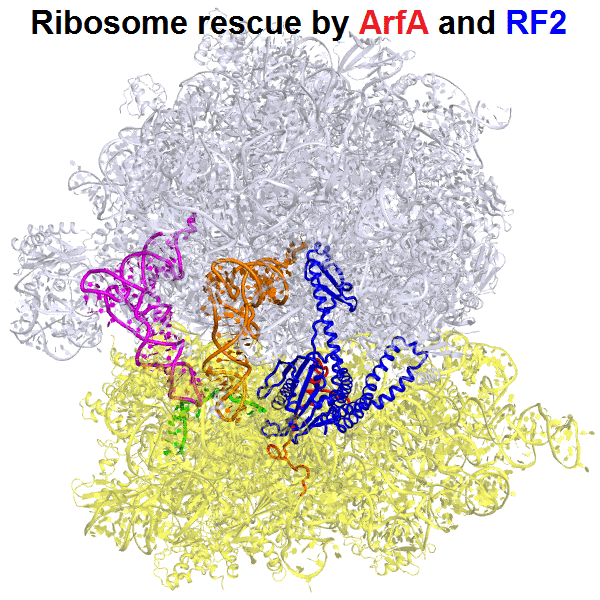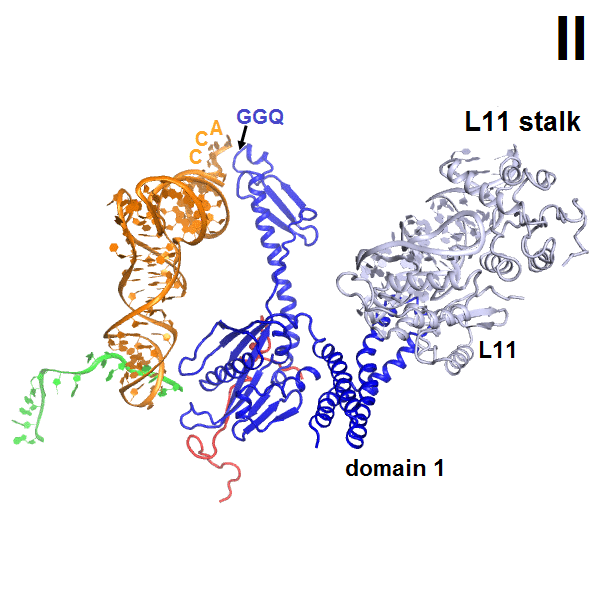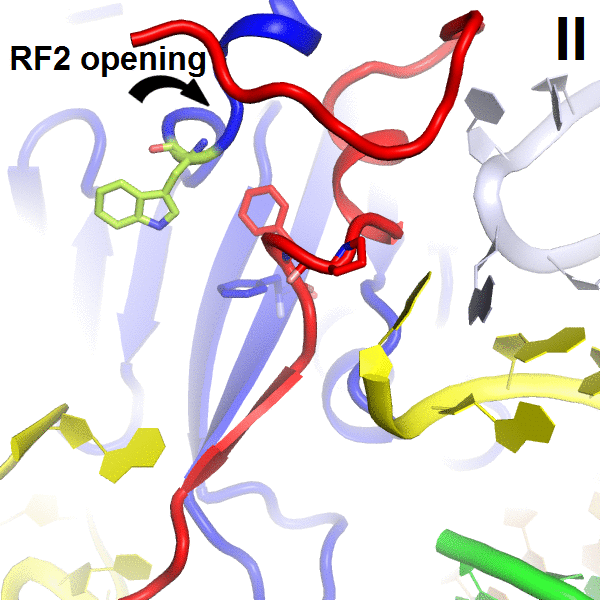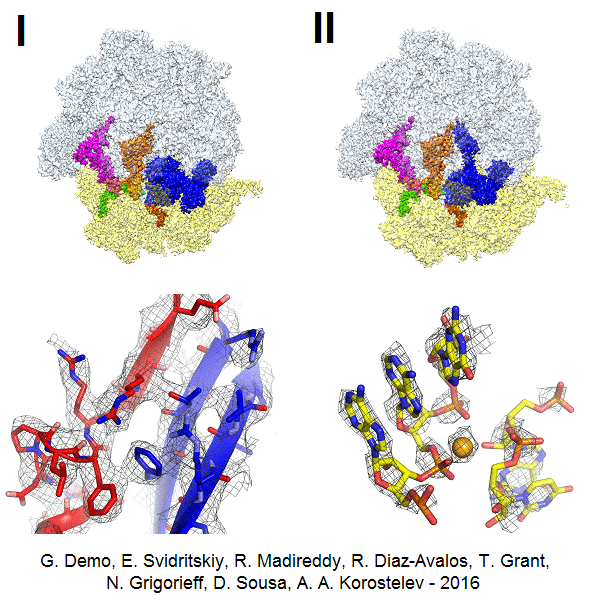
Cellular stress results in translational stalling. Because ribosome synthesis requires large amounts of cellular resources, it is essential that non-translating ribosomes be recycled. Alternative rescue factor A (ArfA) recruits release factor RF2 to hydrolyze peptidyl-tRNA on stalled ribosomes, allowing ribosome recycling. Our ensemble cryo-EM analysis at 3.2 Å resolution revealed the dynamics of the 70S•ArfA•RF2 system, in which ArfA senses stalling due to mRNA truncation (Demo et al, "Mechanism of ribosome rescue by ArfA and RF2". eLife. 2017).
This work visualized the conformational activation of RF2 on the ribosome.
Click on the image above to see an animation showing activation of RF2 by ArfA.