Current Research in Jennifer Wang's Laboratory
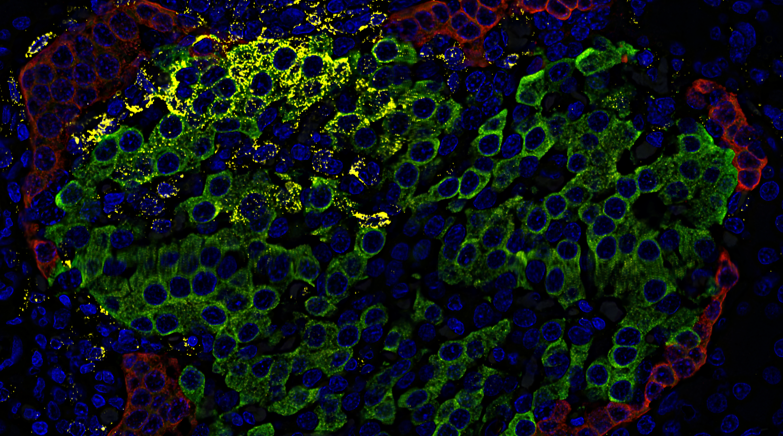
RNA in situ hybridization defines the spatial distribution of the prediabetic rat islet cell transcriptome
Type 1 Diabetes Research
Dr. Wang’s ongoing research involves the study of human islets as well as rodent models to identify autoimmune and inflammatory pathways that could potentially be blocked to prevent disease development.
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is caused by insulin deficiency resulting from the destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells. Breakthrough T1D-funded research in Dr. Wang's lab is investigating how viral infection may trigger T1D. Using primary and stem-cell derived human islets, both in vitro or engrafted in mice in vivo, as well as rat models of diabetes, our research is looking at relationships between infection, innate immunity, inflammation, and islet function.
Respiratory Virus Research
Dr. Wang studies innate immune responses to respiratory viruses, including influenza and SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19.
Influenza A virus (IAV) causes a highly contagious acute respiratory illness that is responsible for significant morbidity and mortality in humans. IAV causes both seasonal epidemics and worldwide pandemics. Our current research, funded by the Department of Defense, studies immune responses during infection with influenza IAV, respiratory syncytial virus, or SARS-CoV-2. We're actively engaged in human clinical studies to prevent and treat human respiratory viruses.
Wang Lab Determines JAK Inhibitors Show Promise in Preventing Type 1 Diabetes

The Wang lab discovered that type I interferon signaling is not the sole driver of the disease. They published a study that tested JAK inhibitors and identified a potential preventive treatment that blocked diabetes development in their novel rat models of Type 1 diabetes.
LEARN MORE
Shedding New Light on the Relationship Between Viral Infections and Type 1 Diabetes

The Wang lab defined how deleting components of the innate immune antiviral response alters immune cells to protect against autoimmunity using a novel rat model of Type 1 diabetes to investigate viruses as possible triggers of the disease.
LEARN MORE