Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs): Biochemistry and Chemical Biology of Protein Citrullination
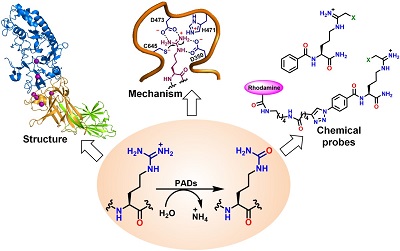
Dr. Paul Thompson and Dr. Santanu Mondal, a Postdoctoral Fellow in Dr. Thompson lab, published excellent review of PAD structure, mechanism and inhibition. Congratulations!
Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs): Biochemistry and Chemical Biology of Protein Citrullination
Citrullination is a post-translational modification of arginine, catalyzed by a group of cysteine hydrolases called protein arginine deiminases (PADs – PAD1, 2, 3 and 4). Protein citrullination plays important roles in epigenetic regulation of gene expression, neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation and DNA-damaged induced apoptosis. Despite the physiological roles, aberrant protein citrullination leads to variety of autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, ulcerative colitis (UC), Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS) and certain cancers. In this Account, we summarize our 13 years efforts to understand the structure, mechanism and biochemistry of PADs. We also discuss the development of various reversible and mechanism-based covalent PAD inhibitors, activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) probes to monitor PAD activity as well as to discover potent inhibitors by high throughput screening.
Pubmed ID: 30844238
Read the full article: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00024
All Dr. Thompson's publications can be viewed on myNCBI : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/browse/collection/46555446/?sort=date&direction=Descending
