UPRmt signaling and regulation.
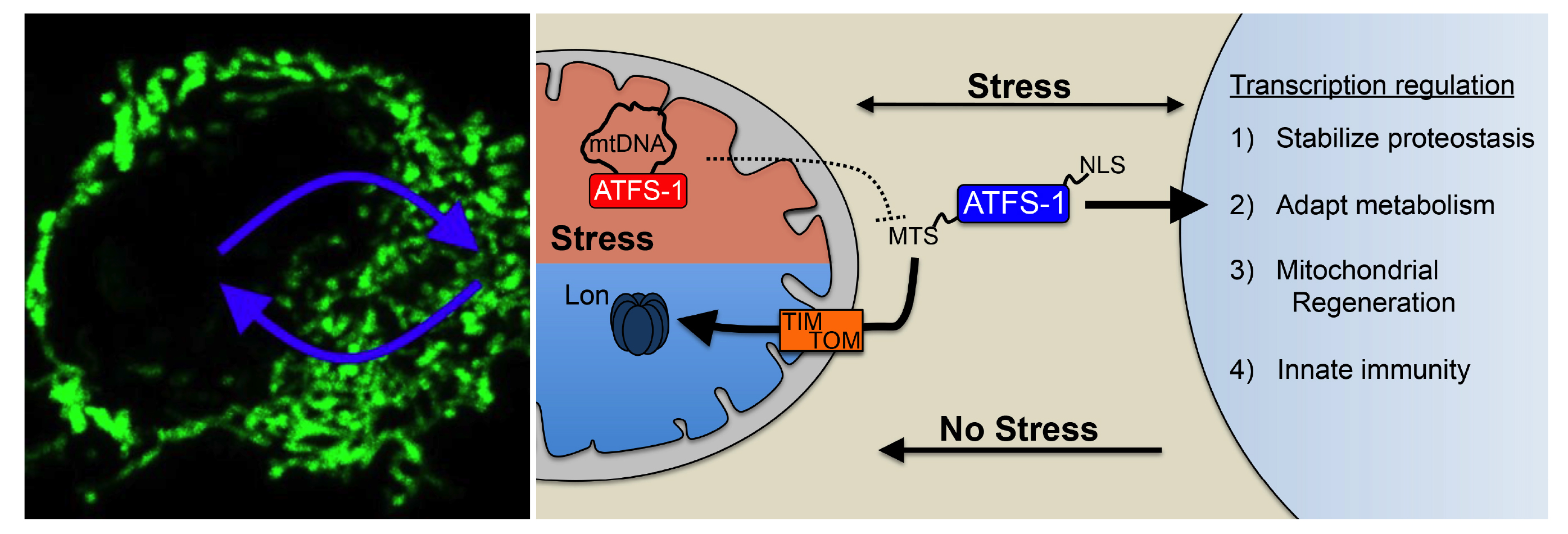
The UPRmt is regulated by the transcription factor ATFS-1 in C. elegans1 and ATF5 in mammals2. ATFS-1 is expressed at a high level but is rapidly imported into healthy mitochondria and degraded by the protease Lon. But, during mitochondrial dysfunction such as OxPhos damage or an increase in unfolded proteins, mitochondrial protein import efficiency is reduced causing proteins to accumulate in the cytosol. Because ATFS-1 has a nuclear localization sequence, it then traffics to the nucleus to induce the UPRmt, which includes transcripts that both, promote survival, and ultimately recover mitochondrial activity. Thus, the cell simply utilizes the protein import capacity of the total pool of organelles as a sentinel of mitochondrial function3,4.
Building on this model of organelle partitioning as a means to regulate adaptive transcription, a number of import issues remain to be resolved including:
How does organismal or cellular growth and nutritional status impact UPRmt activity?
Is mitochondrial import efficiency regulated or an outcome of mitochondrial damage?
References:
1Nargund AN*, Pellegrino MW*, Fiorese CJ, Baker BM, Haynes CM. (2012) Mitochondrial import of ATFS-1 regulates mitochondrial UPR activation. Science. Aug 3;337(6094): 587-90. PMID: 22700657
2Fiorese CJ*, Schulz AM*, Lin YF, Rosin N, Pellegrino MW, Haynes CM. (2016) The transcription factor ATF5 mediates a mammalian mitochondrial UPR. Current Biology. PMID: 27426517
3Haynes CM, Fiorese CJ, Lin YF.(2013) Evaluating and responding to mitochondrial dysfunction: the mitochondrial unfolded protein response and beyond. Trends in Cell Biology. July;23(7): 311-318. PMID: 23489877
4 Lin YF, Haynes CM. (2016) Metabolism and the UPRmt. Molecular Cell. Mar 3:61(5): 677-682. PMID: 26942672
